Vestibular function tests evaluate how effectively your balance system is functioning. These tests help identify potential weakness or asymmetries in the inner ear, which could be contributing to your dizziness or balance issues.
Our assessments are bulk billed with a referral from your GP or medical specialist.
Please allow 2 hours for this appointment.
Your appointment will include the following tests:
Video Head Impulse Test
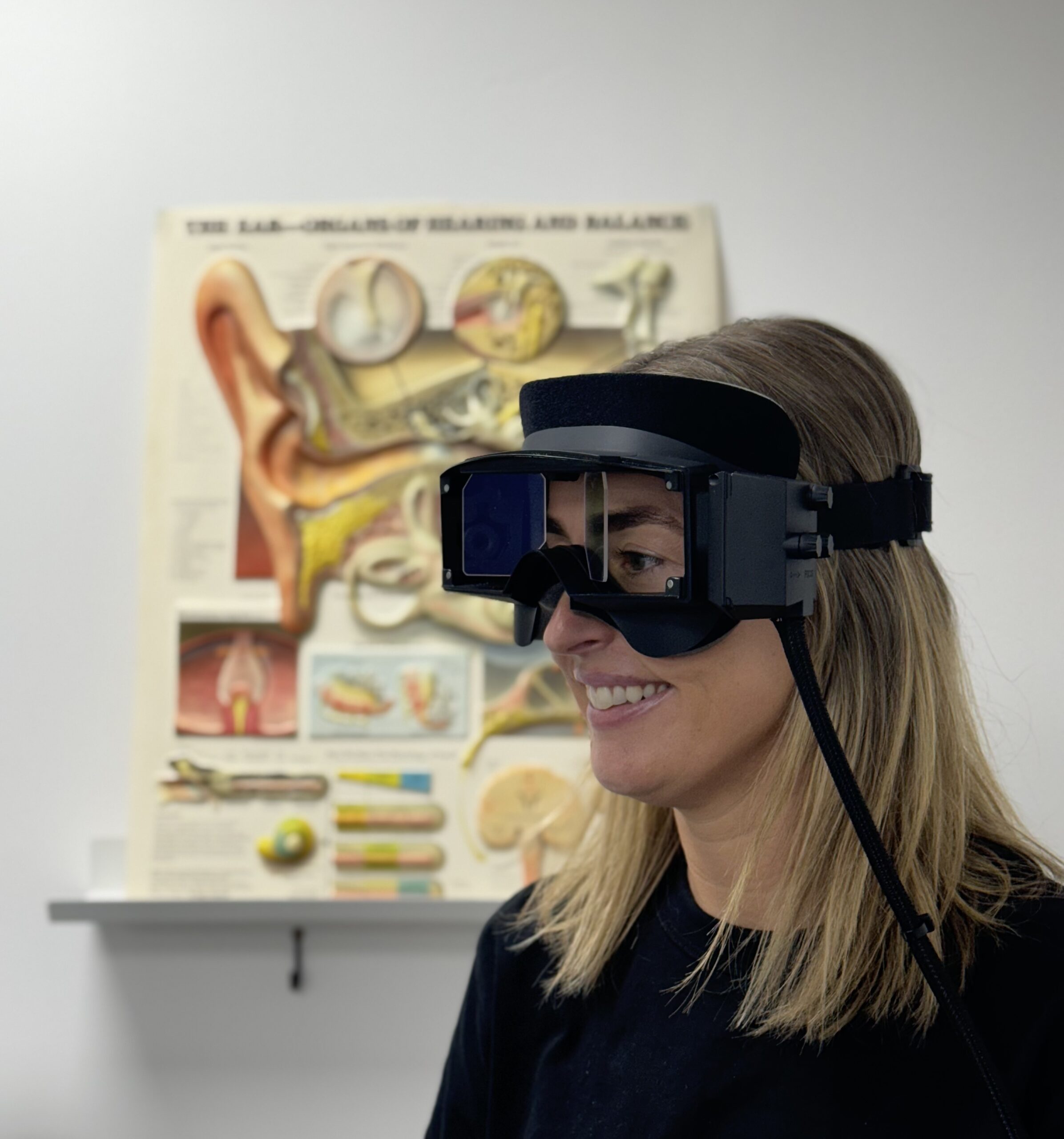
What is it? A quick, and non-invasive test used to assess the function of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR), which helps stabilise your vision during rapid head movements. It allows us to evaluate the function of the semicircular canals in the inner ear.
What is involved? You will wear a lightweight set of goggles with a high-speed camera and motion sensors that track head and eye movements in real time. You will focus on a target while your head is moved in small, quick motions left, right, up, or down, depending on the semicircular canal being tested.
Videonystagmography (VNG)
What is it? A series of tests that are performed while using an infrared camera to monitor and record your eye movement. Eye movements can provide signs of vestibular dysfunction and/or neurological problems and are a key step in diagnosing vestibular disorders.
What is involved? You will wear a pair of goggles while we ask you to follow a target that is either still or moving.
Positional testing
Videonystagmography is also used to observe eye movements during Dix-Hallpike testing which assesses for the most common cause of vertigo, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
Eye movements are recorded to characterise nystagmus (a jerky eye movement). This allows us to correctly diagnose which semicircular canal is affected so we can perform the appropriate treatment. The most common treatment is the Epley manoeuvre.
Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMPs)
What is it? VEMP testing is used to evaluate whether the gravity sensing organs and associated nerves are intact and functioning normally. Responses in these tests are measured from muscles in the neck and under the eyes.
What is involved? You will be asked to lie down. Recording pads will be placed in various positions including your neck, under your eyes, forehead and chest. One test involves lifting and holding your head off the pillow while loud clicks are played in your ear. A second test involves looking upwards while vibration pulses are placed on your forehead.
Auditory Brainstem Response
What is it? The ABR measures how the nervous system sends an acoustic message from the ear to the brain.
What is involved? You will be lying down and an earphone will play a series of clicks into your ear for roughly 2 minutes at a time. The good news is you do not need to do anything for this test and can even fall asleep. The test usually takes 8-10 minutes.
Audiometry (Hearing tests)
What is it? An assessment of your hearing levels. Hearing evaluations are an important part of vestibular diagnostics because the inner ear contains both hearing and balance organs. We also perform tympanometry and sometimes acoustic-reflex testing which can help detect problems in the middle ear.
What is involved? Earphones are used to present tones at different pitches and levels for you to respond to when these sounds are heard. Bone-conduction involves sending the tone directly to the inner ear using a device behind your ear. Bone-conduction testing is used to determine if a hearing loss is related to the outer, middle or inner ear. Testing with words may include repeating words in quiet or in the presence of background noise. Audiometry is essential for diagnosing conditions such as semicircular canal dehiscence and Ménière’s disease.
Additional Tests for Ménière’s disease
If you require further testing to investigate the possibility of Ménière’s disease then we will arrange a second appointment for you. The additional tests that will be performed include;
Electrocochleography
What is it? A test of the electrical activity generated by the cochlear and eighth nerve. The response generated by the cochlea is often increased in Ménière’s disease while the response from the eight nerve remains unchanged. Results are calculated as a ratio and can be used to assist with a Ménière’s diagnosis.
What is involved? Ear drops are placed into the ear then drained out again before a lead with a recording ball is placed into the ear and gently onto the eardrum. A series of clicks are played into the ear. This test is fully automatic so you do not need to do anything.
Caloric Testing
What is it? Caloric testing uses changes in temperature within the inner ear to individually stimulate the horizontal semicircular canals (HSCCs). This test allows us to assess the function of the HSCCs and can also be used in conjunction with the video head impulse testing to assist in Ménière’s diagnosis.
What is involved? You will lie down wearing googles. Warm and cool air is blown into the ear for roughly 60 seconds. This test can cause you to feel like you are turning. We record your eye movements using videonystagmography as described above.
Results, management and reports
We explain the results of our tests during the appointment and will talk you through any recommendations we might have for further investigation or management of your symptoms.
We then provide a comprehensive report summarising our findings as well as our recommendations back to your referring doctor.
What can I expect during an appointment?
Watch the following videos to see how an appointment is run: